10 KiB
+++ title = "Entity Component System - It's not a system" outputs = ["Reveal"] +++
Entity Component System
What is (an) ECS?
- {{< frag c="unnecessary" >}}
- {{< frag c="useful" >}}
- {{< frag c="not a system" >}}
{{% note %}}
Talk about structure of presentation here:
- define terms like "entity", "component", "system"
- go over other approaches to "motivate" ECS
- main 3 game engines will be mentioned (Unity, Unreal, Godot)
- talking about the level of programming engines, not games
{{% /note %}}
What are entities?
What are entities?
What are entities?
- Objects in a game (or simulation)
- Can have different behaviours
- {{< frag c="Basically everything" >}}
INHERITANCE
{{% section %}}
{{< slide transition="none" >}}
Inheritance
graph TD;
Entity-->MoveableEntity;
Entity-->PhysicsEntity;
{{% note %}}
Entity: Basic information like transform and mesh in our example MoveableEntity: Entity with functions to move with and support animations PhysicsEntity: Walls, Falling Boulders and stuff; Colliders and Gravity
{{% /note %}}
{{< slide transition="none" >}}
Inheritance
graph TD;
Entity-->MoveableEntity;
Entity-->PhysicsEntity;
MoveableEntity-->Character;
PhysicsEntity-->BoxColliderEntity;
{{% note %}}
Entity: Basic information like transform and mesh in our example MoveableEntity: Entity with functions to move with and support animations PhysicsEntity: Walls, Falling Boulders and stuff; Colliders and Gravity
{{% /note %}}
{{< slide transition="none" >}}
Inheritance
graph TD;
Entity-->MoveableEntity;
Entity-->PhysicsEntity;
MoveableEntity-->Character;
Character-->Player;
Character-->NPC;
PhysicsEntity-->BoxColliderEntity;
{{% note %}}
Entity: Basic information like transform and mesh in our example MoveableEntity: Entity with functions to move with and support animations PhysicsEntity: Walls, Falling Boulders and stuff; Colliders and Gravity
{{% /note %}}
{{% /section %}}
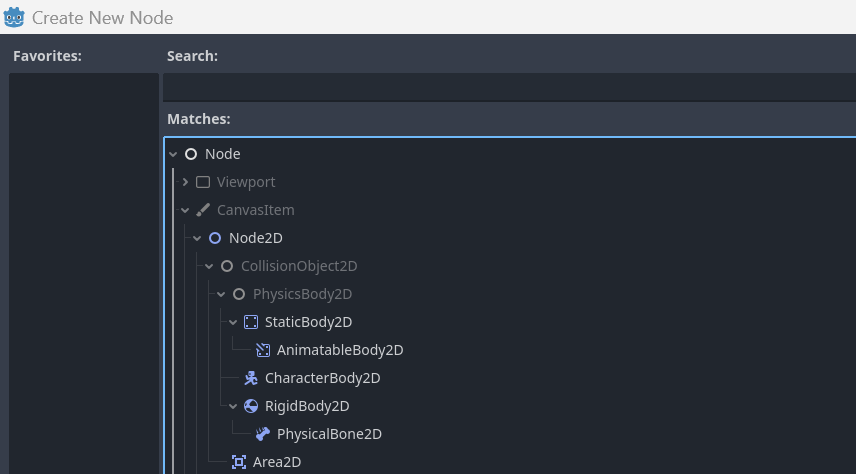
Godot
Godot Code
class Node2D : public CanvasItem {
...
}
.
.
.
class PhysicsBody2D : public CollisionObject2D {
...
}
class CharacterBody2D : public PhysicsBody2D {
...
}
{{% section %}} {{< slide transition="none" >}}
Inheritance
graph TD;
Entity-->MoveableEntity;
Entity-->PhysicsEntity;
MoveableEntity-->Character;
Character-->Player;
Character-->NPC;
PhysicsEntity-->BoxColliderEntity;
MoveableEntity-->Vehicle;
{{< slide transition="none" >}}
Multiple Inheritance
graph TD;
Entity-->MoveableEntity;
Entity-->PhysicsEntity;
MoveableEntity-->Character;
Character-->Player;
Character-->NPC;
PhysicsEntity-->BoxColliderEntity;
MoveableEntity-->Vehicle;
BoxColliderEntity-->Vehicle;
{{% /section %}}
Godot
- uses hierarchy instead
- child nodes as "components"
What are components?
- {{< frag c="Split entities from behaviour" >}}
- {{< frag c="Data associated with a certain "behaviour"" >}}
COMPOSITION
Composition
graph LR;
EntityA-->BoxColliderComponent;
EntityA-->StaticMeshComponent;
EntityB-->SphereColliderComponent;
EntityB-->DynamicMeshComponent;
EntityB-->PlayerControllerComponent;
linkStyle default stroke:lime,stroke-width:4px;
Composition
- {{< frag c="Entities have minimal data and behaviour" >}}
- {{< frag c="Entities hold their components or references to them" >}}
{{% fragment %}}
class Component;
class Entity {
//...
private:
std::unordered_map<std::type_info, Component*> m_components;
}
{{% /fragment %}}
{{% note %}}
Wanted to have a look at Unreal Source code, but...
{{% /note %}}
Unreal
Code in Unreal's AActor class5:
/**
* All ActorComponents owned by this Actor. Stored as a Set as actors may have a large number of components
* @see GetComponents()
*/
TSet<TObjectPtr<UActorComponent>> OwnedComponents;
/**
* Get all components derived from class 'ComponentType' and fill in the OutComponents array with the result.
* It's recommended to use TArrays with a TInlineAllocator to potentially avoid memory allocation costs.
* TInlineComponentArray is defined to make this easier, for example:
* {
* TInlineComponentArray<UPrimitiveComponent*> PrimComponents(Actor);
* }
*
* @param bIncludeFromChildActors If true then recurse in to ChildActor components and find components of the appropriate type in those Actors as well
*/
template<class ComponentType, class AllocatorType>
void GetComponents(TArray<ComponentType, AllocatorType>& OutComponents, bool bIncludeFromChildActors = false) const
{
typedef TPointedToType<ComponentType> T;
OutComponents.Reset();
ForEachComponent_Internal<T>(T::StaticClass(), bIncludeFromChildActors, [&](T* InComp)
{
OutComponents.Add(InComp);
});
}
{{% note %}}
next, Unity, but...
b. Distributing Examples You may Distribute Examples (including as modified by you) in Source Code or object code to any third party.
{{% /note %}}
Unity
{{% note %}}
- can't confirm what Unity uses (no source found)
- interface suggests composition
- Unity DOTS?
{{% /note %}}
What are systems?
- {{< frag c="███████████████████" >}}
- {{< frag c="█████████████████" >}}
- {{< frag c="████████████████████" >}}
{{% note %}} We'll talk about it later. {{% /note %}}
Entity Component System
{{% note %}}
ECS is Data-Oriented rather than Object-Oriented
{{% /note %}}
Entity Component System
- {{< frag c="split components even more from entities" >}}
- {{< frag c="entities are minimal data" >}}
- {{< frag c="components store data associated with certain behaviours" >}}
- {{< frag c="components aren't managed by their entities" >}}
{{% note %}}
- entities can just be ids
- component manager
{{% /note %}}
What are systems?
- {{< frag c="main way of interacting with components" >}}
- {{< frag c="loop over every component of a type" >}}
- {{< frag c="e.g. Rendering System, Physics System..." >}}
{{% note %}}
- due to systems, want to optimise for iterating over components of a type
{{% /note %}}
Examples:
{{% fragment %}}
One thing known to most is that EnTT is also used in Minecraft. Given that the game is available literally everywhere, I can confidently say that the library has been sufficiently tested on every platform that can come to mind.
{{% /fragment %}}
{{% note %}}
Bevy ECS used for Tiny Glade
{{% /note %}}
Cache
| CPU | L1 | L2 | L3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pentium N4200 | 96 KiB | 128 KiB | 2 MiB |
| i7 14700HX | 1800 KB | 28 MB | 33 MB |
{{% note %}}
top: silas' laptop bottom: mine
Mine are probably also KiB/MiB, because Windows is doing Windows things
Cache Locality less important with newer cpus, but will probably still lead to benefits. Storing data contigous should reduce cache misses, since accesses are more predictable. Collider Component may have 3*float64 position + 4*float64 rotation + 3*float64 size + 10*float64 miscellanious = 160 Byte 300 of those = 48 KB 500 of those = 80 KB
{{% /note %}}
How to implement it in C++
Entities:
//one possibility
typedef uint_32t UID;
typedef UID Entity;
How to implement it in C++
Components:
A std::flat_map is a fitting datatype.
{{% fragment %}}
| GCC libstdc++ | Clang libc++ | MSVC STL |
|---|---|---|
| not implemented | partially implemented | not implemented |
{{% /fragment %}}
How to implement it in C++
Components:
class ComponentManager{
template<typename comp_type> requires std::is_base_of<Component, comp_type>
foreachComponent(std::function func){
//...
}
template<typename comp_type> requires std::is_base_of<Component, comp_type>
addComponentToEntity(Entity entity){
//...
}
//some type of ComponentMap store
}
{{% note %}}
possible ComponentMap store:
std::unordered_map<std::typeid, std::size_t> m_typeOffsetMap;
void* m_componentMaps;
{{% /note %}}
How to implement it in C++
ComponentMap:
template <typename component_type>
class ComponentMap
std::vector<component_type> m_values;
std::unordered_map<Entity, size_type> m_mapping;
Links
- Images from deathgenerator.com
- Helpful thesis by Toni Härkönen
- Data Structures for Entity Systems: Contiguous memory
-
https://br.ign.com/league-of-legends-wild-rift/89123/feature/wild-rift-tudo-sobre-o-lol-mobile ; Image: Riot Games ↩︎
-
https://pressakey.com/gameinfos,4981,screenshots,,,Age-of-Empires-Definitive-Edition,.html ↩︎
-
Screenshot: Godot Engine ↩︎
-
Engine/Source/Runtime/Engine/Classes/GameFramework/Actor.h ↩︎
-
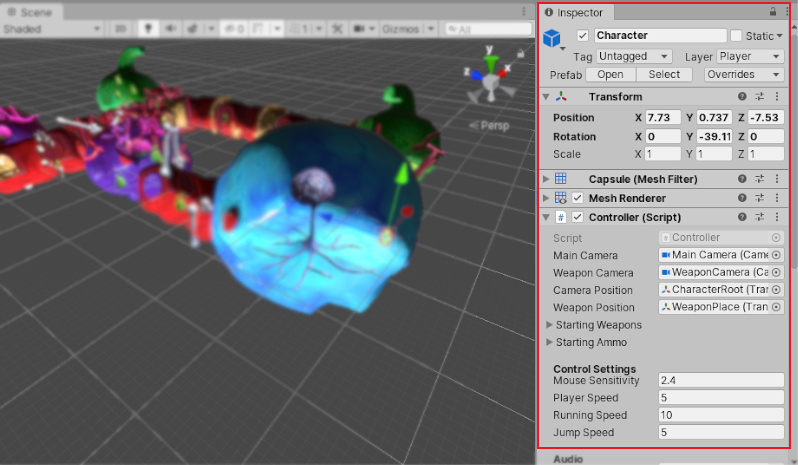
https://docs.unity3d.com/6000.0/Documentation/Manual/UsingTheInspector.html ↩︎